The Myanmar education system consists of three main levels: primary education, secondary education, and higher education. Primary education lasts for 4 years, followed by 4 years of lower secondary school and 2 years of upper secondary school.
Students are required to complete primary education until the age of 9, with international standards implemented in schools until the age of 15 to 16. The Myanmar education system has seen many developments, adopting modern curricula that align with today’s evolving needs.
Read also: Pay by Card, The Smarter Way to Pay International Invoices!
Myanmar Education System
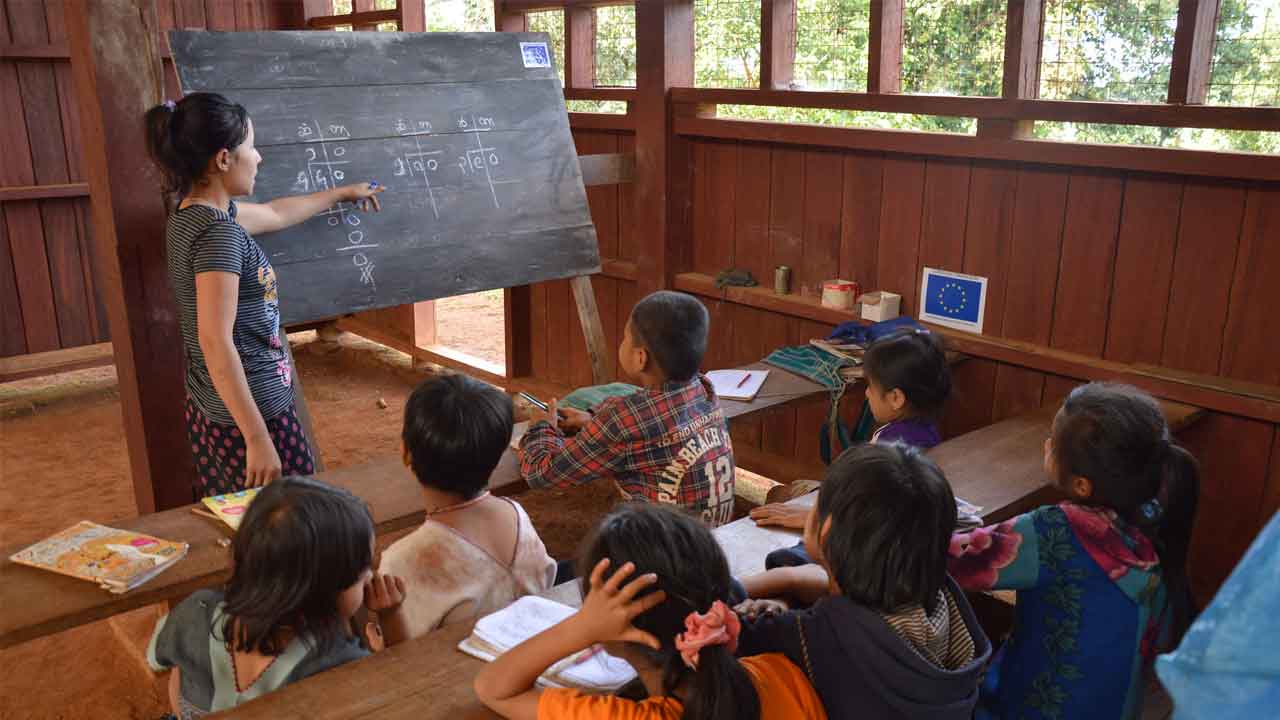

The Myanmar education system is administered by government institutions and the Ministry of Education. Professional institutions and universities in Myanmar are overseen separately by two entities: the Department of Higher Education and the Lower Myanmar Department of Higher Education.
These departments are headquartered in Yangon and Mandalay, respectively. The education system is modeled after the British system, largely due to nearly a century of British and Christian influence in the country. As a result, most schools were historically run by the government, although recently there has been a rise in privately funded English language schools.
Education is compulsory until the end of primary school, usually around 9 years old. Internationally, students are expected to stay in school until the age of 15 or 16. Myanmar is home to 101 universities, 9 colleges, 12 institutes, 146 higher education institutions, and 24 state colleges.
Transfez, Easy Money Transfers to 70+ Countries Worldwide
Myanmar Education Curriculum
Myanmar’s education curriculum is structured into four main stages. The school system includes 5 years of primary school, 4 years of secondary school, and 2 years of upper secondary or vocational school.
To progress to a higher level, students must pass final exams administered by their schools. All basic and higher education institutions are overseen by the Ministry of Education.
Basic education management is handled by three departments of basic education and the Department of Educational Planning and Training, following directives from Myanmar’s legal and organizational authorities.
Education Levels in Myanmar

The Myanmar education system is divided into key subsectors within the broader education sector: basic education and higher education.
1. Basic Education Subsector
- Preschool Education
Early childhood education and care focus on nurturing children under age 5—socially, physically, spiritually, and mentally. It includes preschool programs for children aged 3 to 5, and various childcare services starting at age 3. These programs are offered through community centers, family-based environments, and integrated parenting and educational activities.
- Primary Education
Primary education is compulsory and lasts 5 years, including one year of kindergarten or grade 1. It’s split into two cycles: lower primary (grades 1–3) and upper primary (grades 4–5).
Children generally start primary school at age 5, although many begin grade 1 after age 6. At the end of primary school, students must pass an exam to progress to the next level.
- Secondary Education
Secondary education is the second stage of basic education, comprising two cycles: lower secondary (grades 6–9, 4 years) and upper secondary (grades 10–11, 2 years). At the end of this stage, students must take the basic education high school examination.
The culmination of the basic education program is the matriculation exam. Technical and vocational education is also offered through agricultural schools, technical high schools, vocational and trade schools.
2. Higher Education Subsector
Myanmar has 64 higher education institutions under the Ministry of Education and another 92 under 11 other ministries, including selection and public service training bodies. All higher education institutions are state-funded.
Higher education institutions focus on a variety of disciplines such as economics, business, arts and sciences, law, foreign languages, teacher training, engineering, maritime studies, computer science, defense, forestry, agriculture, veterinary science, and more. They offer programs at the undergraduate, postgraduate diploma, master’s, and doctoral levels.
Institutions under the Ministry of Education have also established human resource development centers, which offer retraining and ongoing development programs from short certificate courses to full master’s programs.
Two departments of higher education are responsible for managing and coordinating institutions under the Ministry of Education. Although universities may be administratively under other ministries, academic policies and higher education administration are overseen by two boards chaired by the Minister of Education: the Central University Council and the University Academic Council.
Download the Transfez App
The Transfez app helps you transfer money abroad more quickly, affordably, and efficiently. Transfez Business also supports your company in conducting international transactions. Whether you’re sending money to family overseas for education, work, or travel, Transfez is here to help. The app is available on both Android and iOS. Download it now!